What is the relationship between the wear rate of Drum Brake Linings and the usage environment?
Drum Brake Linings are key components in the automotive braking system, and their performance and du...---17 Oct
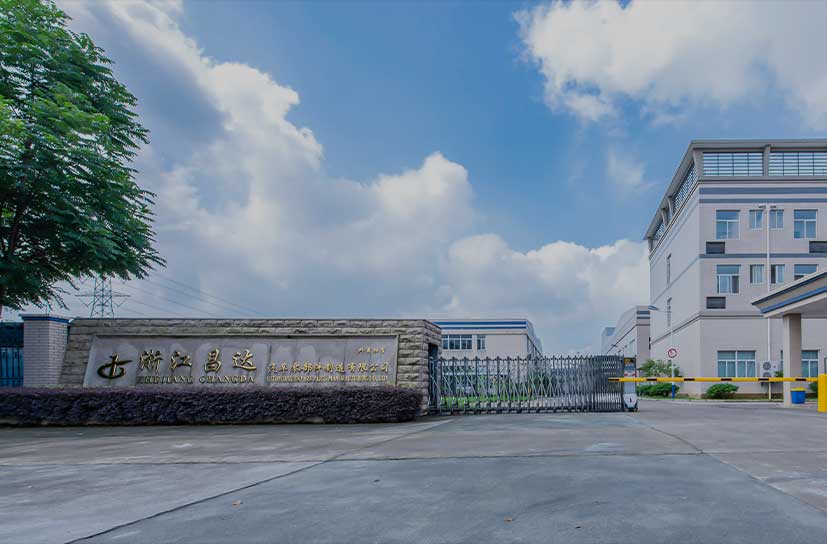
READ MOREZhejiang Changda Automobile Part Making Co., Ltd. is located near the scenic summer resort Mount Mogan Scenic Spot, 309 Changhong East Street, Deqing High tech Development Zone, close to Hangzhou Nanjing Expressway, Hangzhou Nanjing High-speed Railway, China National Highway 104, Provincial Highway 09 and Xuancheng–Hangzhou railway, close to Hangzhou, Shanghai, and Ningbo, the water-land-air transportation is very convenient. The company was founded in 2006 and is a national high-tech enterprise with over ten invention patents and utility model patents. The total investment is 53 million yuan, covering an area of 46000 square meters, including 26000 square meters in the main factory area and 20000 square meters in the branch factory area.
It specializes in the production of drum brake linings, disc brake pads, light/ medium and heavy brake shoe assemblies, and forklift clutch assemblies. MERCEDES-BENZ Brake Linings Manufacturers and Wholesale MERCEDES-BENZ Drum Brake Lining Company.
The company adheres to the business philosophy of sincerity, trustworthiness, and excellence, and has established a complete product research and development center and advanced testing equipment, equipped with a comprehensive CAD design and CAM manufacturing system. We have taken the lead in introducing high-precision equipment such as domestic first-class CNC batching systems, CNC weighing bag systems, CNC mold hot pressing, forming systems, and CNC grinding processing systems. Supply OEM MERCEDES-BENZ Brake Linings.
The product has passed IATF16949, EU R90 product quality management system certification, American Motor Vehicle Manufacturer Certification service agency AMECA product certification, American Green Testing Center DOT/FMVSS 121D, and South Africa SABS VC8503 testing recognition. Through advanced design and manufacturing, as well as a comprehensive management system, product quality has been reliably guaranteed. We sincerely welcome communication and cooperation with domestic and foreign manufacturers.
Company founded
Investment amount
Covering area
Covering countries

 Company Video Overview
Company Video Overview
Drum Brake Linings are key components in the automotive braking system, and their performance and du...---17 Oct
READ MOREDrum brake linings play a crucial role in vehicle safety and performance, particularly under challen...---10 Oct
READ MOREThe design and function of the Brake Shoe Assembly in terms of the transmission of braking force are...---01 Oct
READ MOREThe environmental impact of disc brake pads in terms of disposal and recycling is significant and mu...---23 Sep
READ MORE